AMS 105: The American West
|
AMS 105: The American West |
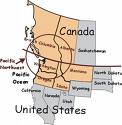
B. Regional Definitions
Great Plains:

In terms of American immigrants into the United States the Great Plains is the first traveled by pioneers. However, they went through the Great Plains and called it the Great American Desert. The Great Plains runs from the 98th Meridian to the Eastern slope of the Rockies around 105th Meridian. In the North it begins in Alberta and Saskatchewan to Texas. At 98° the altitude is about 500’ above sea level and as you travel west toward Denver, Colorado, you reach 5,000’ above sea level; thus Denver is called the ‘Mile High City.’ This transition is from the Low Plains to the High Plains. The Plains economy is a mix of grain crops with cattle and later is a source of coal, gas and oil. Much of the human occupation is low population densities with some of the largest ranches and farms with thousands of acres. Most of the original family-owned farms and ranches are now owned by huge corporations. There are three great river systems that run from the Rockies to the Mississippi, they include:
Great Plains Rivers
|
Main River |
Tributaries |
Total Length to Mississippi |
States |
|
Missouri |
Yellowstone, Cheyenne, Little Missouri, Niobrara, Platte, Kansas |
2315 mi To St. Louis, MO |
MT-ND-SD-NB-IO-MO |
|
Arkansas |
Little Arkansas, Cimarron, Canadian, Verdigris, Neosho |
1459 mi |
CO-KA-OK-AR |
|
Red |
Wichita, Little |
1290 mi |
NM-TX-OK- |
These rivers were a haven for wildlife and provided irrigation sources. Later, these rivers were damned up for flood control, irrigation and hydroelectric power. Most of the reservoirs also provided fishing and boating resorts.
In terms of immigrant groups there were many Europeans that settled the Great Plains after the Civil War. In Canada there were Scot and English farmers. In the Dakotas many German and Scandinavian immigrants came to farm. In Nebraska and Kansas various Central European and Eastern European immigrants came to settle along the railroads. In some cases entire towns in Europe relocated to new towns in the Plains. Oklahoma was originally Indian Territory and was one of the last frontier areas to be open. The Cherokee Strip Land Run occurred in 1893. Those that cheated and snuck out the night before were called "Sooners." Texas drew many German immigrants in the Eastern farmlands and Texas hills, but many Scotch-Irish settled the Great Plains regions from Tennessee & Kentucky after the Civil War. The southern areas of Texas were already settled by the Spanish and later Mexican immigrants.
Most of the cities in the Great Plains were cow towns with rail hubs for shipping beef. Denver was a mining town, being in the high plains on the eastern edge of the Rocky Mts.
Great Plains Cities
|
City |
Population |
Notes |
|
Bismark,ND |
56,619 |
|
|
Wichita, KS |
353,823 |
Founded 1864 |
|
Oklahoma City, OK |
528,042 |
Land rush 1889 |
|
Ft. Worth, TX |
603,337 |
Military post 1849 |
|
San Antonio, TX |
1,236,249 |
Span. garrison 1718 |
|
Laredo , TX |
203,212 |
Founded 1755, Span |
|
Billings, MT |
96,977 |
|
|
Cheyenne, WY |
55,362 |
1867 first surveyed |
|
Denver, CO |
556,835 |
1858,gold prospectors |
|
Albuquerque, NM |
484,246 |
Founded 1706, Span. |
|
Amarillo, TX |
180,791 |
1887 water hole and cattle shipping point,1888 settled |
|
El Paso, TX |
592,099 |
Founded 1598, Span. |
Southwest:

The American Southwest is comprised of high desert plateaus of juniper scrub and pinyon pine or low desert regions with creosote scrub and saguaro cactus. Initially, the Spanish and later European immigrants were limited to large acreage ranches. However, minerals were also found, especially copper, silver, and turquoise. Later, immigrants emulated the ancient Hohokam (prehistoric Am. Indian) in the Gila and Salt River areas by using the ancient irrigation canals for farming. This became today’s Phoenix area. The Native American and Hispanic influence on the Southwest is extensive and includes architecture, food, dress, fiestas, and art.
Southwest Cities
|
City |
Population |
Notes |
| Santa Fe, NM |
68,041 |
Founded in 1598, Span. |
| Albuquerque, NM |
484,246 |
Edge of Plains |
| Phoenix, AZ |
1,418,041 |
Founded 1867 |
| Tucson, AZ |
512,023 |
1775 as presidio, Span. |
| Flagstaff, AZ |
57,038 |
1855 first surveyed, 1876 first settled |
Southwest Rivers
|
River |
Tributaries |
Total Length |
States |
| Rio Grande | Pecos R.; Rio Conchos R. | 1,885 mi
 Big Bend NP |
NM, TX, MEX |
| Colorado | Gila R. and Salt R. | 1,450 mi
 Hoover Dam |
CO, UT, AZ, CA |
Rocky Mountain States:

The Rocky Mountains and the Continental Divide run on a SE – NW diagonal beginning just above Taos, New Mexico, to the Idaho panhandle and into Canada. This mountainous region was first exploited by immigrants for timber and mining. Also, hydroelectric plants were built along the rivers. Later, resort towns like Aspen, CO became important economic sources, especially for skiing. The Rocky Mountains eastern side is the end of the Great Plains and at 5,000- 9,500 ' above sea level you experience a shift from sagebrush scrub to juniper scrub and Aspen and Cottonwood along the rivers as you climb in altitude. As you get higher you run into various confers with different species at different altitudes. At around 8,500 trees give out to alpine meadows and heath. The Missouri and Arkansas drainages start in these eastern slopes and run through the Plains to the Mississippi River. Most of the earliest people were the mountain men who eliminated the beaver throughout the West by the early 1800s. They were followed by the mining interests and timber companies.
Pacific Northwest:

The Pacific Northwest is comprised of intermountain deserts (Plateau) that have two great rivers running from the Rocky Mountains through the High Cascades into the Northwest Coast.
Northwest Coast Rivers
|
Main River |
Tributaries |
Total length to Pacific Ocean |
States |
| Fraser | Thompson, Lillooet, Adams |
850mi |
Continental Divide, BC to Vancouver, BC |
| Columbia | Duncan, Kutenai, Okanogan, Snake, Yakima, Walla Walla, Umatilla, Klickitat |
1243mi |
Continental divide/Columbia Lake, BC to Pacific Ocean between WA & OR |
These rivers had salmon running all the way upstream into the Rocky Mountains. On the Western slope of the High Cascades there is a virtual temperate rainforest with over 200" rainfall/annum in the Olympic Peninsula of Washington State and Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. Some of the fertile valleys, such as Willamette, Oregon, and Walla Walla, Washington, provided for early immigrant farmers before the Civil War. Also, timber, minerals, and hydroelectric power plants became part of the economy of the Pacific Northwest.
In terms of people, many English, German, Scot-Irish, and Irish families were some of the earliest settlers. However, the Pacific Coast acted as a border for many Russian, Asian and Pacific Islander people that immigrated to the US and Canadian shores.
Pacific Northwest Cities
|
City |
Population |
Notes |
|
Vancouver, BC |
587,891 |
Settled 1860, Fraser R. Gold Rush |
|
Seattle, WA |
571,480 |
Settled 1851, lumber town |
|
Spokane, WA |
196,721 |
Settled in 1872 |
|
Boise, ID |
190,122 |
Ft. Boise 1830, city 1864 |
|
Portland, OR |
533,492 |
Settled 1845 trade, lumber |
California:

California is the only state that is a specific region of its own. It begins with pockets of temperate rainforests of Coastal Redwoods and Sequoia along the coast and in the Sierras. The Coastal Redwoods in the Northwest part of California and the Central Coast in Santa Cruz/Big Sur represent some of the oldest temperate rainforests in the world. Strange creatures like the Pacific Giant Salamander and the Banana Slug still lurk in this ancient forest, untouched by the Ice Age. However, most of California is made up of Riparian Oak Woodland and Scrub brush. In the Southern deserts (Mohave and Anza-Borrego) more severe deserts are comprised of Joshua Tree (a Yucca), Yucca, Creosote – Juniper scrub. Death Valley is the severest desert with the lowest point in the U.S. (-282' below sea level).



California is separated by the High Sierras from the Basin, but is quite variable in climate and terrain. California’s attraction to American Indians and European immigrants is its incredibly mild climate due to the mountains and warm Japanese current coming from the northwest in the Pacific The Spanish missed the gold, but the Anglos found it in 1849. After the Gold Rush, farming and ranching became important. Initially, farming in the Salinas Valley provided a great output of crops. Later, the Great Central Valley produced the bulk of crops. Now, the Imperial Valley with Colorado R. irrigation has also been added to the areas of farming.
California Rivers
| Main River | Tributaries | Total length | States |
| Sacramento | Feather, Yuba, Mokelumne, Consumnes | 377 mi | CA-Outflow at Suisun Bay-SF Bay |
| San Joaquin | Tuolumne, Merced, Fresno, Kern | 350 mi | CA-Outflow at Suisun-SF Bay |
| Eel | North, Middle, South Forks | 200 mi | CA-Lake Co-Humboldt Co |
| Russian | 100 mi | CA-Mendocino Co to Sonoma Co | |
| Salinas | Namcimento R. and San Antonio R. | 155 mi | CA-Outflow Salinas, Ca runs south to north from San Luis Obispo Co to Monterey Co |
| Santa Ana | 90 mi | San Bernardino Co to Riverside Co with outflow in Orange Co | |
| San Luis Rey | 55 mi | CA-San Diego Co Outflow Oceanside CA | |
| San Diego | 52 mi | CA- San Diego Co Outflow to San Diego Bay and Mission Bay |
In some parts of Northern California and the Sierras timber was and is a principal product. As of 1970 California resources were suppressed by tourism with its diverse cities, media, amusement parks, and National Parks.
The first European immigrants were the Spanish in 1542 and later 1769. Later, Mexican immigrants settled as California for a brief time was a frontier of the Republic of Mexico. Later, with the Mexican War (1846-48) and the Gold Rush (1849) other Europeans poured into California from everywhere. The fishing off the California coast brought South American, Italian American, and Portuguese Americans to San Francisco, Los Angeles, and San Diego.
California Cities
|
City |
Population |
Notes |
|
Sacramento |
454,330 |
1839 Ft Sutter; Gold Rush trading 1849 |
| Stockton | 289,789 | Founded 1849 |
|
Fresno |
457,719 |
Founded 1872 |
|
Bakersfield |
323,213 | Founded 1869 |
|
San Francisco |
744,230 |
Span. Mission 1776 |
|
Oakland |
397,976 |
Span. 1820, current name Anglo 1854 |
|
San Jose |
904,522 |
Span. 1777 Mission and first CA Pueblo |
|
Santa Cruz |
54,593 | Spanish Mission 1791 |
|
Santa Barbara |
90,473 | Span. Presidio 1782, Mission 1785, city 1850 |
|
Los Angeles |
3,845,541 |
Span. 1781 |
|
Long Beach |
476,564 |
Span. 1784, harbor area 1884 |
|
San Diego |
1,263,756 |
Span. Mission 1769 |
The Great Basin:

This is a high desert area with no rivers running into a sea/ocean. The soil is very alkaline. Parts of Idaho, Oregon, California, Utah and all of Nevada make up this desert. Mining has been a principle economic resource, and later gaming became state legal and has afforded the Great Basin with revenue.
Great Basin Cities
|
City |
Population |
Notes |
|
Reno, NV |
197,963 |
Founded 1857 |
|
Las Vegas, NV |
534,847 |
Founded by Mormons (LDS) 1855, railroad 1903 gaming legalized 1931 |
|
Salt Lake City, UT |
181,743 |
Founded 1847 by Mormons(LDS) |
The miners of the Great Basin were a mixed lot, many from the Eastern United States or Europe, especially Wales and Eastern Europe. Basque sheepherders also came to the Basin and for many years drove along the Eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. In 1847 Mormons (LDS), under Brigham Young, emigrated from New York via Illinois to settle in Utah with Salt Lake City as cultural and religious center.
In 1931, partly due to the Depression and mining output, the state of Nevada legalized gaming. Also, a considerable amount of nuclear tests were conducted in Nevada. The Bonneville Salt Flats brought people from around the world to break land speed records.
C. Natural History & Ecosystems
When you study any particular area, like the American West, the natural history is an important factor in human adaptations to their environment. This includes the geologic history, geography (including climate) and native wildlife. Often this information comes from other supportive courses in geology, biology, and geogrphy. I have created a separate page/ link to give some background to help you understand the base. We use some of the larger ecosystems to cover the wildlife of the American West. The ecosystems are somewhat compatible with the sub regions covered in your text Many Wests. These are as follows:
| ECOSYSTEM | AMERICAN WEST SUBREGIONS |
| Great Plains Prairie | Plains & Prairie Midwest |
| Montane | Rocky Mountains, California Sierras, Cascades |
| Sonoran Desert | Southwest, Southern California |
| Pacific Coast Rainforest | Northwest Coast, Northern California |
Next: II. Historical Realities
Back To Main Page
Copyright © S. J. Crouthamel 2013