Money, money! $$. Elasticity of demand is a tool that helps firms make more money. It is a number that aids sellers of a product or service to increase the revenue (defined as price times quantity sold) of the firm.
Imagine you had a business and that by changing the prices of your products you end with more money! Elasticity is defined as the responsiveness in quantity demanded in percent given a percent change in price.
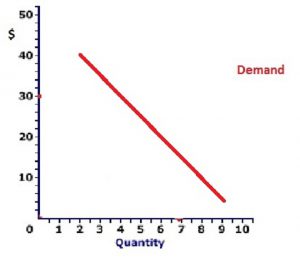
Imagine the scenario above – 50% sale at your local store. Check the table below:
| Demand for blouses | Demand for blouses with 50% sale |
|
|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 2 blouses | 6 blouses |
| Price | 40 dollars | 20 dollars |
The formula for elasticity is:
In the example above Q1 = 2 blouses and P1 = $40, Q2 = 6 blouses and P2 = $20 (50% off). The video below will show how to calculate the value of elasticity:
The values of the elasticity formula will help the decision maker determine how to change prices in order to increase total revenue. In the previous example:
| PRICE | QUANTITY | TOTAL REVENUE | VALUE OF ELASTICITY |
|---|---|---|---|
| $40 | 2 | $80 | 1.45 |
| $20 | 6 | $120 |
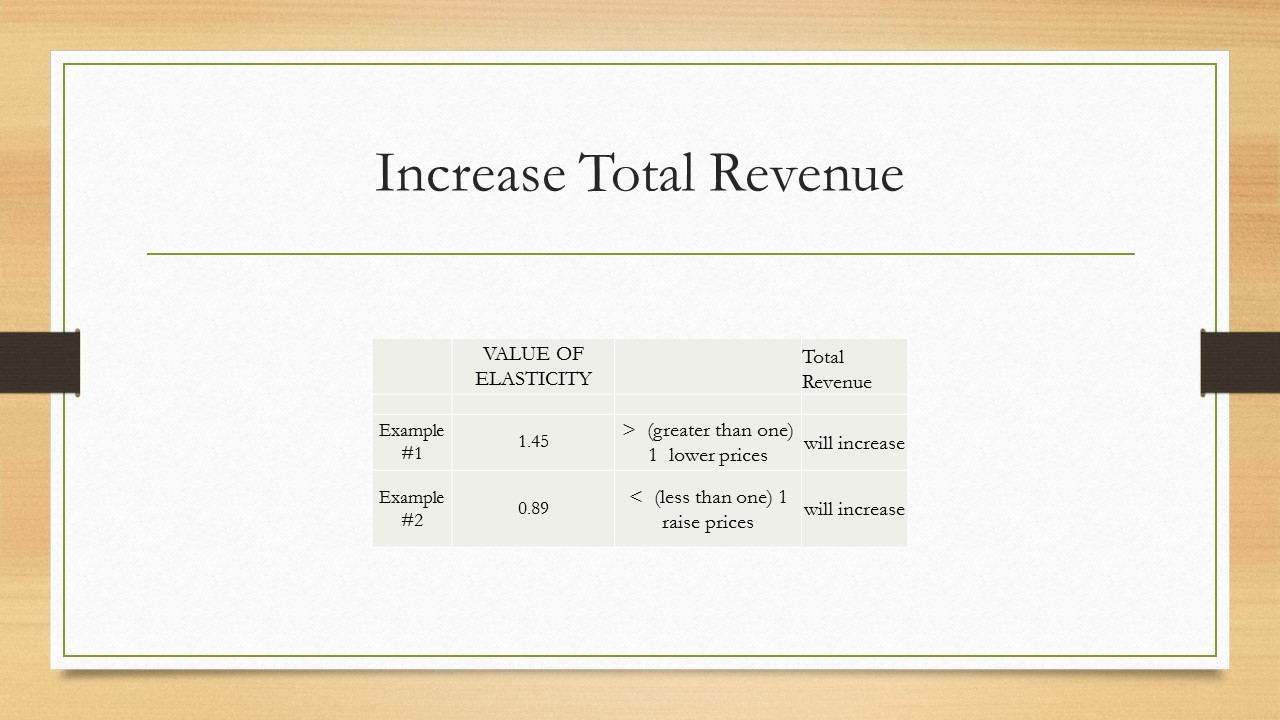
The value of elasticity in this example, 1.45, tells us that this portion of this demand curve is elastic so that if we lower the price to $20 and we sell 6 blouses the total revenue is $120 as opposed to the original price of $40 and 2 blouses and total revenue of $80. Economist label this a relatively elastic demand when the value of the formula – 1.45 in this example – is greater than 1. Lower price and increase total revenue $$ We like more money!
However sometimes when prices go down – a firm makes less money 🙁 Let’s follow an example:
| PRICE | QUANTITY | TOTAL REVENUE | VALUE OF ELASTICITY |
|---|---|---|---|
| $2.85 | 15 | $42.75 | 0.89 |
| $2.65 | 16 | $42.40 |
Using gasoline as an example – we see that as the price drops the total revenue decreases – what is going on? Economist label this a relatively inelastic demand when the value of the formula – 0.89 in this example – is less than 1. This is what elasticity is designed for – using the value of elasticity a firm can determine whether to raise/lower prices to increase total revenue. This decision is made based upon the value of the elasticity formula – let’s review our examples from above:
 There is one more possibility – that the firm changes prices and revenue remains the same! Economists called this the unitary value (= 1) of elasticity – however we will not expand on this case since it is very rare.
There is one more possibility – that the firm changes prices and revenue remains the same! Economists called this the unitary value (= 1) of elasticity – however we will not expand on this case since it is very rare.
The short clip below will summarize how the value of elasticity helps a firm increase total revenue: